The cycle of pain can feel relentless, trapping individuals in a loop where physical and emotional pain feed off each other. But this cycle is not unbreakable. Recognizing the connection between these two forms of pain is the first step toward effective management. As a pain management specialist, I emphasize the importance of addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of pain simultaneously. Understanding that they are intertwined allows us to create a more holistic approach to treatment.
Breaking the cycle begins with awareness. Patients must be made aware of how their emotional state can exacerbate their physical pain and vice versa. Education is crucial—understanding that feelings of sadness, anxiety, and stress can intensify physical pain empowers patients to take proactive steps in managing their emotional health alongside their physical symptoms. This approach not only helps in alleviating immediate pain but also reduces the likelihood of chronic pain developing over time.
Strategies for Managing Physical Pain
Managing physical pain requires a multifaceted approach. One size does not fit all, as each patient’s pain experience is unique. Here are some strategies that can be effective in managing physical pain:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen can be effective for mild to moderate pain. For more severe pain, prescription medications such as opioids or muscle relaxants may be necessary. However, these should be used cautiously and under the supervision of a healthcare provider due to the risk of dependency.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program that targets the specific areas of pain, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent future injuries.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide temporary relief from pain. Heat helps to relax tense muscles and improve blood flow, while cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs the affected area.
- Massage Therapy: Regular massages can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation, all of which contribute to pain relief. This therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic conditions like Greenbelt spinal stenosis.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain. Acupuncture is believed to stimulate the body’s natural painkillers and has been shown to be effective in managing various types of pain, including back pain and osteoarthritis.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain are essential for managing physical pain in the long term. Simple changes, such as adopting a more ergonomic posture at work or incorporating regular stretching into your daily routine, can make a significant difference.
Strategies for Managing Emotional Pain
Just as physical pain requires a variety of strategies, emotional pain must be addressed with care and precision. Emotional pain management is crucial, as unresolved emotional distress can intensify physical pain. Here are some effective strategies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of psychotherapy that helps patients recognize and change negative thought patterns that contribute to emotional pain. By addressing these thought patterns, patients can learn to cope better with their emotions, reducing their overall distress.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices involve focusing on the present moment and accepting it without judgment. Meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety, which are often linked to both physical and emotional pain.
- Stress Management Techniques: Learning how to manage stress effectively is key to breaking the cycle of pain. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga can help lower stress levels and improve emotional well-being.
- Support Groups and Counseling: Talking to others who are experiencing similar pain can provide emotional relief and a sense of community. Counseling with a mental health professional can also help patients process their emotions and develop coping strategies.
- Creative Expression: Engaging in creative activities such as art, music, or writing can provide an outlet for emotional pain. These activities allow individuals to express their feelings in a non-verbal way, which can be therapeutic and healing.
- Healthy Relationships: Building and maintaining strong relationships can provide emotional support, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation that often accompany chronic pain. Spending time with loved ones, talking openly about feelings, and seeking support can make a significant difference.
Combining Physical and Emotional Pain Management
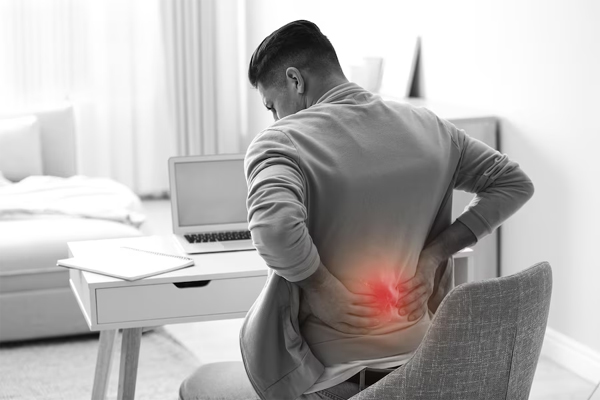

Combining physical and emotional pain management strategies is essential for comprehensive care. When both aspects of pain are addressed simultaneously, patients are more likely to experience relief and an overall improvement in their quality of life. Here’s how combining these approaches can work:
- Integrative Care: Combining physical treatments like physical therapy with psychological support like CBT can provide a well-rounded approach to pain management. For instance, while physical therapy addresses the physical source of pain, CBT helps manage the emotional distress that often accompanies it.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices like yoga and tai chi blend physical movement with mindfulness, offering a dual approach to pain management. These practices not only help strengthen the body but also calm the mind, reducing both physical and emotional pain.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the connection between physical and emotional pain empowers them to take control of their health. When patients understand that addressing their emotional health can alleviate physical symptoms, they are more likely to engage in holistic pain management practices.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Each patient’s pain experience is unique, so treatment plans should be tailored to address both physical and emotional aspects of pain. This might include a combination of medication, physical therapy, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes.
In Conclusion
The interplay between physical and emotional pain is complex, but understanding this relationship is crucial for effective pain management. By addressing both aspects of pain, patients can break the cycle that keeps them trapped in a state of constant discomfort. As a pain management specialist, my goal is to provide patients with the tools and strategies they need to manage their pain holistically, improving not only their physical health but also their emotional well-being. By combining physical and emotional pain management techniques, we can offer a more comprehensive and effective approach to treatment, ultimately leading to a better quality of life for those suffering from chronic pain.