Gum disease, a chronic bacterial infection, poses a significant threat to oral health, leading to bleeding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and even tooth loss if left untreated. As a leading cause of tooth loss in adults, gum disease has far-reaching consequences, also impacting overall health by increasing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Fortunately, a range of effective treatment options at the dental office in Encinitas exist, from non-surgical interventions like professional cleaning and scaling to surgical procedures such as gum grafting and bone grafting, as well as advanced treatments like regenerative procedures and dental implants.
With the right treatment approach, you can regain control of your gum health and enjoy a healthier, happier smile.
Causes of gum disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums.
Other factors can contribute to the development of gum disease, including:
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
- Certain medications
- Poor diet
- Stress
- Grinding or clenching teeth
Misaligned teeth
- Dental work such as bridges or dentures
Additionally, certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing gum disease, including:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Respiratory disease
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
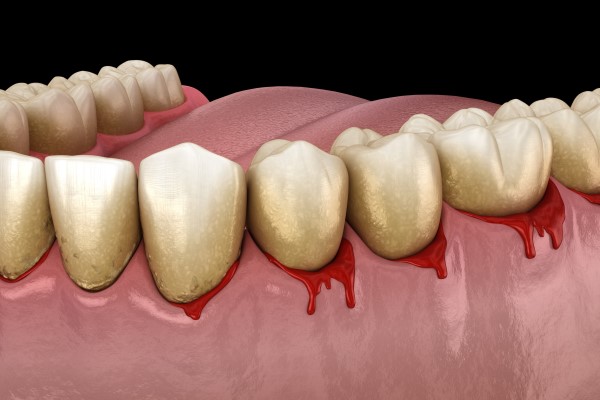
Symptoms of gum disease
Here are the common symptoms of gum disease:
Early Symptoms
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
- Redness and Swelling: Gums that are red, swollen, and tender to the touch.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Sensitive Teeth: Teeth that are sensitive to hot or cold temperatures.
Advanced Symptoms
- Receding Gums: Gums that pull away from the teeth, exposing roots.
- Loose Teeth: Teeth that become loose or feel like they’re shifting.
- Painful Chewing: Pain or discomfort when chewing or biting.
- Visible Plaque: Yellowish plaque or tartar buildup on teeth.
- Gum Pockets: Deep pockets between teeth and gums, trapping bacteria.
- Lost Teeth: Teeth that fall out due to advanced gum disease.
Other Symptoms
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw.
- Gum Abscesses: Painful abscesses or pus-filled pockets in the gums.
- Metallic Taste: A persistent metallic taste in the mouth.
Treatment options for gum disease
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of gum disease, as well as individual needs and health status. A dentist or periodontist will develop a personalized treatment plan to address specific needs.
Here’s an elaboration of the treatment for gum disease:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Professional Cleaning: Deep cleaning to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria.
- Scaling and Root Planing: Removing plaque, tartar, and smoothing roots to prevent further buildup.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics to control infection and reduce inflammation.
- Mouthwash: Antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Laser Treatment: Using lasers to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria, and promote healing.
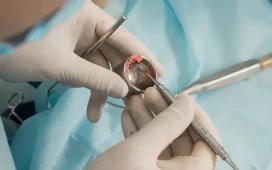
Surgical Treatments
- Gum Grafting: Transplanting healthy gum tissue to replace damaged or receded gums.
- Bone Grafting: Transplanting bone tissue to replace damaged or resorbed bone.
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: Folding back gum tissue to remove bacteria and tartar, and reattaching it to the tooth.
- Crown Lengthening: Exposing more of the tooth to support a crown or filling.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: Transplanting tissue to cover exposed roots or repair gum defects.
Home Care
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups.
- Interdental Brushes: Using small brushes to clean between teeth.
- Waterpik: Using a waterpik to remove plaque and debris.
- Mouthwash: Using antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
Advanced Treatments
- Regenerative Procedures: Using membranes, grafts, or tissue engineering to regenerate lost tissue.
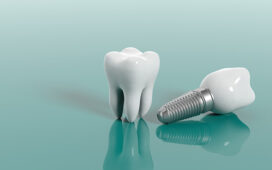
- Dental Implants: Replacing lost teeth with implants.
- Periodontal Plastic Surgery: Repairing gum defects and improving aesthetics.
Gum disease is a treatable condition. Early detection and treatment can reverse the damage and prevent tooth loss. By understanding causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take control of their oral health and prevent gum disease.